The light rays emitted from the sun are crucial for the existence of life on Earth. The formation of light rays starts with the birth of photons in the sun and takes place through a complex process in a plasma state under extreme temperature and pressure. Light rays are made up of tiny packets of energy called photons. Once photons take birth in the sun’s core, it takes around 1-10 lakh years to reach Earth.
Introduction:
Sun is our nuclear powerhouse, our nearest star that emits constant energy in the form of radiation.
This shining ball has plenty of energy and light. It’s impossible to observe its glow from the naked eye. But if we observe from distance say from the Earth using an advanced telescope we see the sun in the form of a scorching gas ball.
The sun is the father of the solar system. It offers necessary things to its children(planets). We depend on the sun for energy, light, and heat which are crucial for the existence of life.
In fact, without star planets doesn’t have their existence. Sunlight runs our solar system by transferring heat continuously. Without light energy, life cannot exist and we will die.
The sun produces a tremendous amount of heat and energy, hence is the power source for all living species on the planet Earth.
Whatever amount of energy our body utilizes to do work is gained indirectly or directly from the sunlight through complex natural biological and chemical processes.
It is interesting to know that the sun is the reason behind the creation of all living species on Earth.
Significance of the sun in the solar system:
 Solar system
Solar system
The sun is a gigantic nuclear bomb that blasts continuously and is filled with upheaval.
If the sun was not there, then there would be no life. Our existence is operated by the energy emitted from the nuclear reaction in the sun’s core.
Light is one of the basic things that build our cosmic order. Light is present in all living beings and is an amazing element that exists in nature. It is the basic and the fastest thing present in the universe, no one can travel faster than light.
How much time light takes to reach Earth from the Sun?
The speed of light is 299,792,458 meters per second.
1 Astronomical unit(AU) is the average distance between the Earth and the sun which is 149,597,870.7 km or 149.06 million km.
velocity = distance/time
Therefore, time = velocity/distance
So it takes 8 minutes and 20 seconds for light rays to reach the Earth.
The 8 minutes and 20 seconds of light travel to the Earth is the end result of its astonishing journey.
In 18 hours, the sunlight reaches the border of our solar system.
Did you know?
The light rays that we see now are older than the first life that originated on the Earth.
The rays originated at least 10 lakh years ago. Light rays took more than 10 lakh years to move from the sun’s core and escape from its outer surface. These light rays originated before the existence of life on Earth.
What is a photon?
Light is made up of energy packets, these single energy packet is called a photon. A photon has no mass(zero mass) and its energy-carrying capacity is proportional to the frequency of the radiation.
So if any object achieves a speed equal to the speed of light, then its mass becomes zero.
We see light rays coming from the sun. These light rays are made up of energy packets called photons. The journey of photons from their formation in the sun’s core to traveling to the Earth is really shocking.
 Sun rays
Sun rays
How are photons created in the sun?
The journey of photons starts with their formation in the sun’s innermost core. Sun is assumed as a gigantic ball made up of hot gas that burns continuously under extreme temperature and pressure conditions. If we travel from the sun’s surface to its core which is lakhs of kilometer distance, we will see more intense hydrogen gas burning inside. The core is the furnace where photons are born in the form of gamma rays photons.
At the center of the core, the birth of photons or light takes place through the process of nuclear fusion.
Nuclear fusion in the sun is the fusion of hydrogen and helium atoms forming bigger atoms together and releasing a tremendous amount of energy. This nuclear reaction is the reason behind the sun’s energy. Helium is formed when two single atoms of hydrogen combine. The nuclear fusion reaction is not easy as two protons that have the same charge which repel each other, so the nuclear fusion reaction should take place in extreme temperature and pressure conditions.
 Atom
Atom
How nuclear fusion takes place inside the sun?
Due to the same charge on the protons, they tend to repel each other and resist fusing each other. In order to fuse the protons, very high energy, high pressure, or high velocity of protons is required and this happens rarely. But how come the sun’s core witnesses continuous nuclear fusion if these conditions are rare? This ideal condition for nuclear fusion that is highly required is high pressure and the sun’s gravity does this.
Sun compromises 99.8% of all the matter present in our solar system. This amount of mass is very high and the reason behind the ultra-strong sun’s gravitational field.
The ultra-strong gravity produces tremendous pressure inside the core that supports nuclear fusion. In this nuclear ball, it is found that each second 10 crore quadrillion quadrillion times hydrogen atoms collide. Among these huge sets of collisions, some collisions are so powerful that hydrogen atoms fuse and release a tremendous amount of energy.
When protons are about to collide with each other under extreme conditions, they lose some mass, and energy is produced from this mass. Each second about 50 lakh tons of matter is converted into energy due to nuclear fusion.
The collisions of protons give birth to an energy burst that consists of an energy packet. The energy packet is tiny but strong and is a flake of light. This energy packet is massless and even tinier than atoms which we call photons.
How is light formed; Matter produces light
Matter produces photons through the nuclear fusion process and the intensity of light depends on the temperature at where it was produced.
In the universe, any material with temperatures above absolute zero degrees celsius produces and emits radiation. We humans continuously produce and emit radiation because our average body’s temperature is 37’C. Our body emits infrared radiation(also called heat radiation) and that is why night vision cameras equipped with infrared sensors capture humans in the dark.
Electromagnetic radiations:
Electromagnetic radiations are waves that carry energy from matter and their strength depends upon the energy present in the matter.
Electromagnetic radiation is classified into 7 types based on their wavelength; radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light(light rays), ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. These radiations have a different energy in their photons.
Light rays that our eyes see are a mixture of seven colors red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet. Visible light which is a spectrum of rainbow lights can be split into seven rainbow colors. Each light color is a photon with different energy.
Our eyes are sensitive to only visible light, and the photons of infrared radiation carry energy lesser than visible light while UV, X-ray, gamma rays, and gamma rays carry higher energy than visible light and our eyes cannot detect. Human eyes can only detect wavelengths from 380 to 700 nanometers.
Our sun which is a hot gigantic ball with hydrogen gas produces all kinds of radiation.
Role of gamma rays:
Gamma-ray is the most potent form of radiation. They are dangerous for life species as they are powerful and can change the form of matter by interacting with the atoms. Gamma rays can change our genetic structure if they penetrate our bodies.
In which layer of the sun are gamma ray photons produced?
In the sun’s innermost core, the formation of photons takes place in the form of gamma rays which is at least lakhs times stronger than the visible rays.
Gamma-ray photons are not directly emitted from the sun’s surface:
After the birth of a photon in the form of a gamma-ray photon in the core, it travels at the speed of light toward the outer surface. At the speed of light, it could easily cross the surface in a couple of seconds but it fails due to obstacles within the sun.
How long does it take for a photon to escape the sun?
On average, a newly formed photon takes 1- 10 lakh years to escape from the outer surface which is quite an overlong journey.
So what is the obstacle that traps a newly formed photon and increases its duration of the journey from 2 seconds to 1-10 lakh years?
The sun is so gigantic, hot, intense, dense, and powerful that it prohibits photons to escape from its surface for 1-10 lakh years. Inside the sun there are many thick layers of dense hydrogen gases burning all the time that do not allow photons to pass and that is why the duration of photons’ journey will not be lesser than thousands of years.
So if you look at the sun, those blazing light rays(bundle of photons) was actually born at least a lakh year ago under the extreme gravity of the sun and other complex processes.
The distance from the inner core to the sun’s surface is 640,000 km. The newly born gamma ray photon should take a couple of seconds to reach the surface but is resisted by the thick clouds of hydrogen gas.
Within the gigantic hot gas ball, there are radiation zones made up of hydrogen gas just above the core. The zones are under extreme compression due to heavy matter loaded on it and this condition persists until the radiation zone gets denser than lead. At this condition, it is highly impossible for photons to pass. The temperature inside the sun is more than 69,44,500’C. At this temperature, the hydrogen gas in the radiation zone converts into a plasma state. Most of the parts in the universe including stars are in the plasma state of matter.
What is plasma?
Plasma is a fourth state of matter that is formed under extreme temperature and pressure. In the other three states of matter; solid, liquid, and gas, electrons revolve around the atom whereas in the plasma state atoms and electrons get separated from each other and atoms no longer influence the electrons.
Our planet Earth is the safest and most stable place but here we can witness a plasma state in the inner core of the sky lightning. The inner temperature of the sky lightning is about 29,400’C. At this temperature, there is a very high chance that atoms and electrons separate and matter attains a plasma state for a short interval of time.
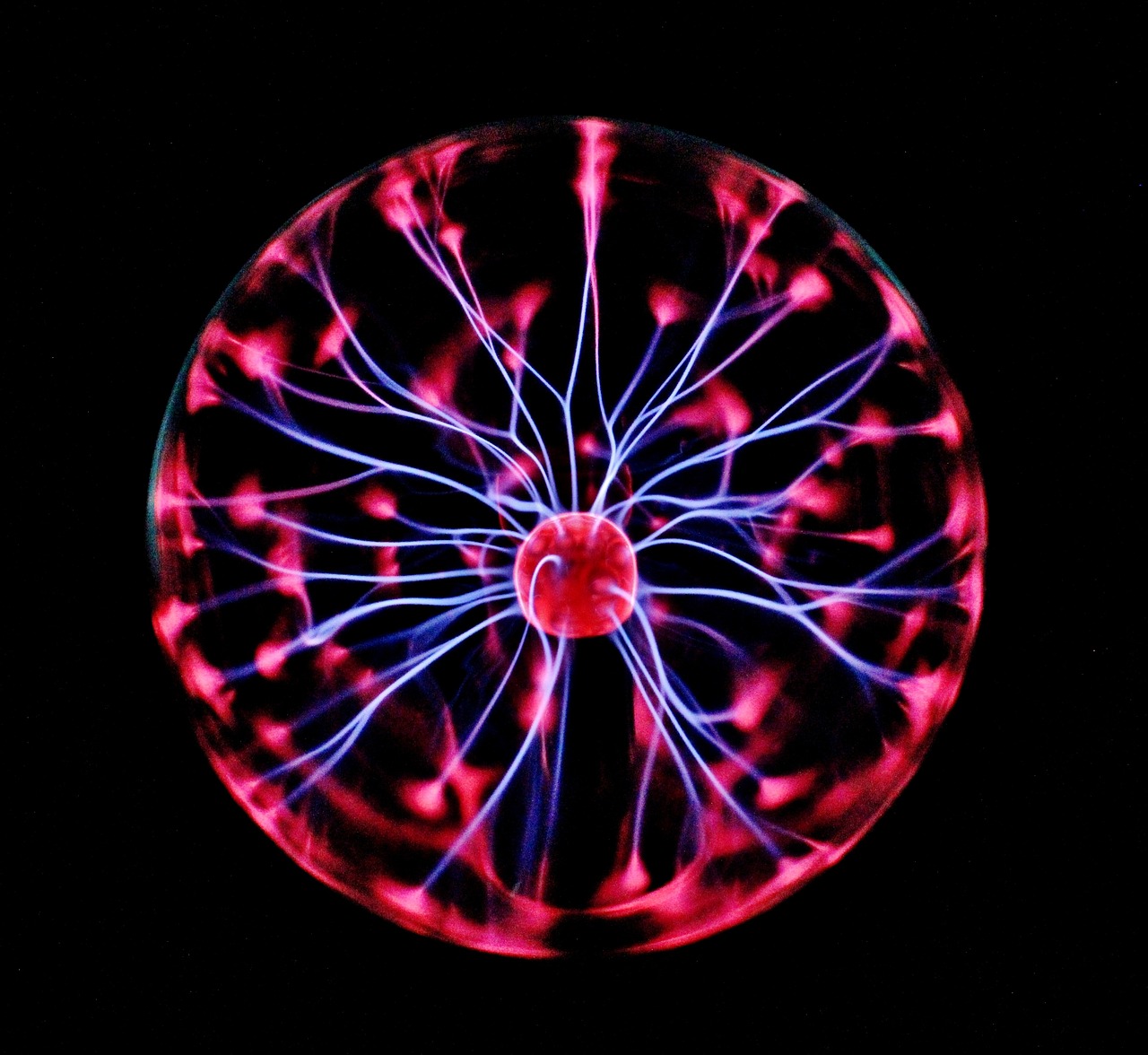 Plasma ball
Plasma ball
But inside the gigantic sun, the plasma state remains for billions of years, and because of this 3,20,000 km deep radiation zone is formed.
Plasma is electrically charged inside the sun, creating a cosmic loop for the photons. Photons can easily pass through electrically neutral atoms but are resisted by electrically charged atoms.
When the photon collides with charged plasma atom, it is absorbed and emitted within a fraction of a second. The photon again keeps on colliding with other plasma atoms in a random direction and the process continues until it reaches the edge of the star with an average duration from thousands to lakhs of years.
The ultimate goal of the photon is to move toward the surface of the sun which is at a lower temperature and come out of the maze of the radiation zone.
In all the subsequent collisions, photons lose some part of their energy and even speed. During the collisions in the radiation zone, the photon changes its form to a less powerful X-ray photon and somehow comes out of the radiation zone. Now the photon has covered almost 3/4th of its journey and is ready to face another obstacle called the convection zone.
Sun’s convection zone lies between the radiation zone and the surface and is about 200,000 km deep.
Some highly excited matter evolves from the core and moves toward the surface producing sound waves. Our current operational satellites are incapable to capture the convention zones but can record the sound waves. These sound waves are spread across the sun’s surface.
These sound waves colliding with plasma produce waves at the surface. These waves keep on hovering over the sun.
The warm gases tend to move up while the cold gas tends to settle down and this catastrophe keeps on going like boiling water. This event happens at a large scale and this gives rise to colliding sound waves.
At the bottom of the convection zone, the X-ray photon collides with plasma atoms and starts boiling. Now the atom holds the photon and flows up due to the heat. Hot atoms also bring the photon to the upper region. Thus X-ray photon comes out of the convection zone through transfer. The convection layer path is simple, fast, and easy and photon spends around 7 days here.
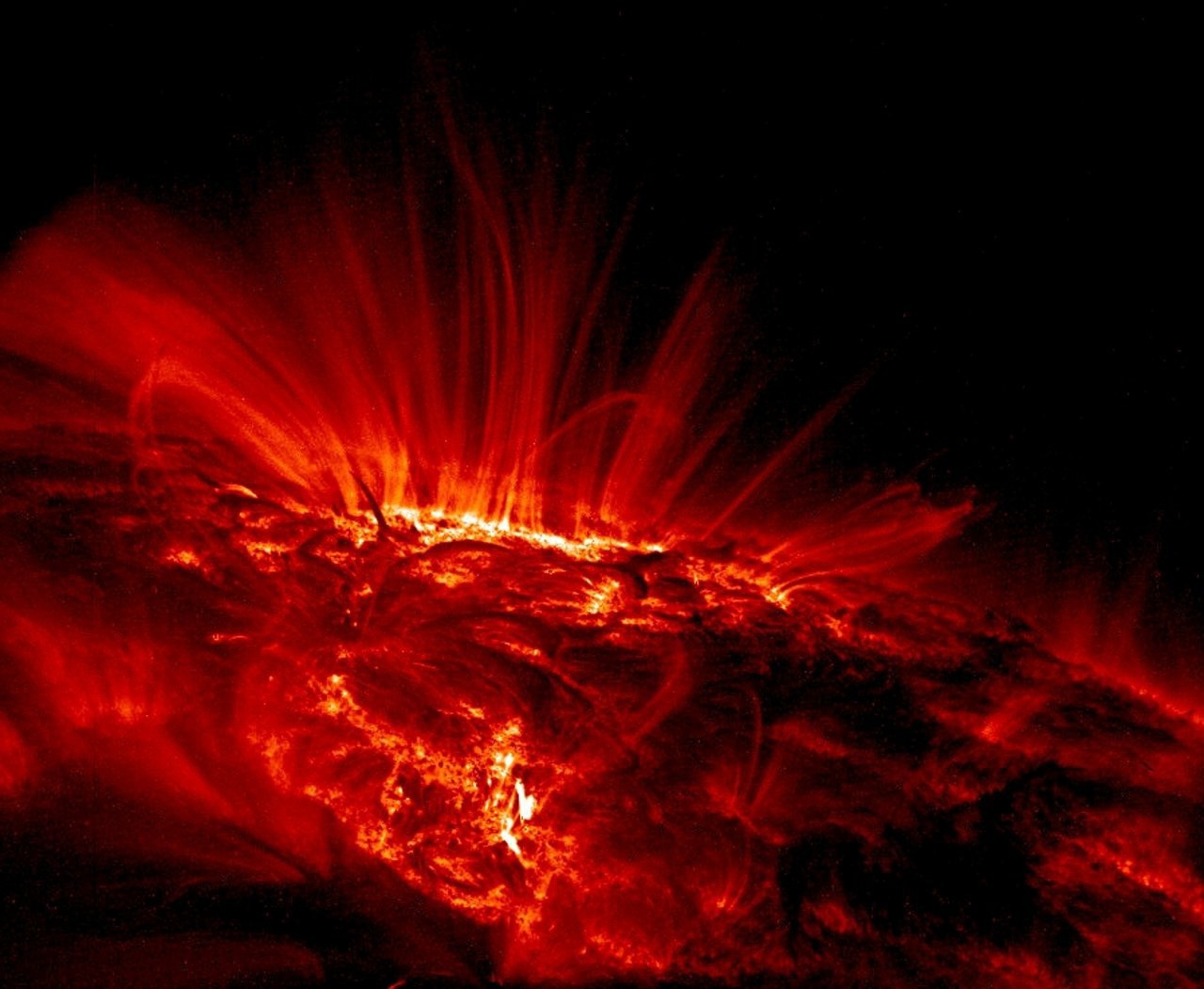 Solar eruption
Solar eruptionThe convection zone changes the X-ray photon into a cool photon of visible light. The lower convection zone’s temperature is 200,000’C and the upper convection zone’s temperature is 5.500’C.
The plasma atom releases the photon in the upper convection zone which now becomes a visible light photon. The visible light photons now heat toward the photosphere. The plasma atoms are also now cooler and again repeat the process of going inside, heating up, and emerging out carrying photons.
The photosphere is the outermost region of the sun and is visible to us. We see visible light coming from the photosphere with our eyes.
While looking with our eyes we see the sun as a calm and stable star but there is a hidden activity in the photosphere that tend to stop photon from jumping out of it.
What is a sunspot?
A sunspot is the dark region of a star where the light photons are trapped. It appears dark and prevents radiation from coming out of its region.
Sunspots are formed when strong magnetic waves from the sun emerge and pass the photosphere. The magnetic field is so strong that it stops the inner hot material’s convective motion from coming to the surface. This gives rise to a dark spot on the sun’s surface, these dark spots are big. Some dark spots can be even bigger than 10 times the size of the Earth.
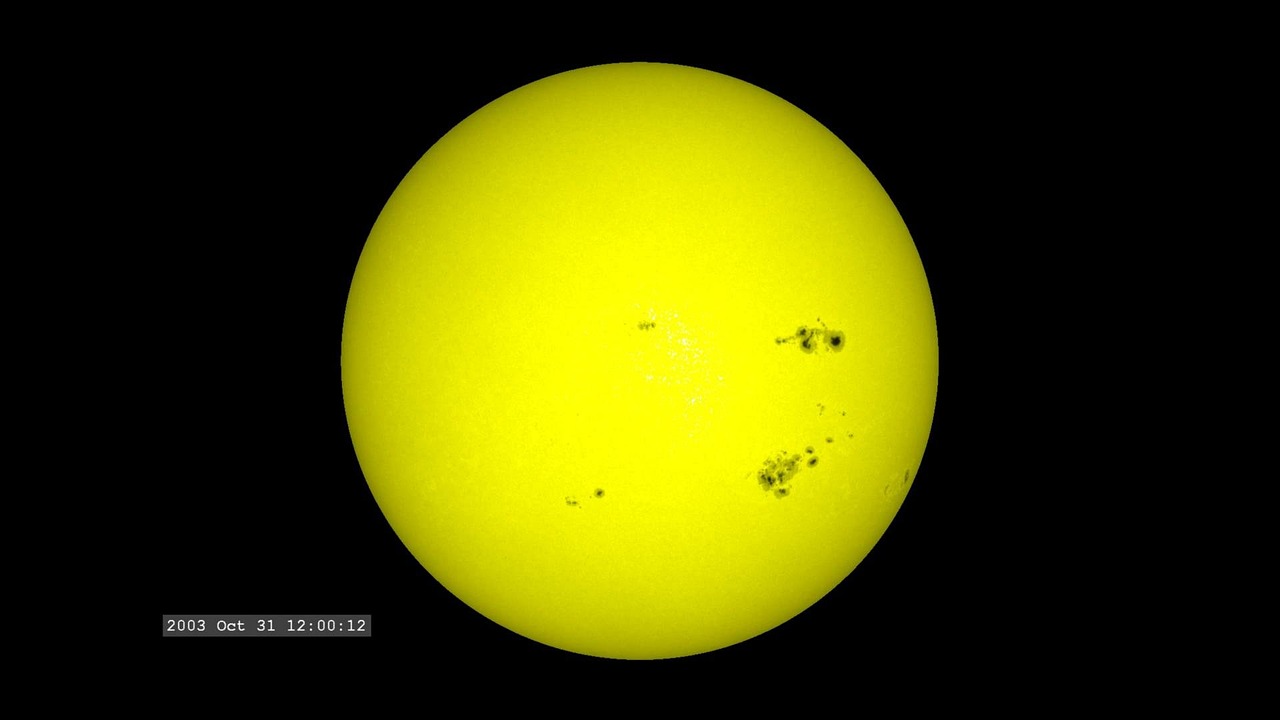 Sunspots
Sunspots
The magnetic waves that create sunspots also become field lines covering the sun. The sun rotates like other planets but planets are rigid where as the sun is a ball of gas. When planets rotate the magnetic field also rotates along with them and the same rule doesn’t apply to the sun. The sun’s equator rotates faster than the poles along with its magnetic field. With variable rotation across the surface, the sun’s magnetic field gets distorted and becomes uneven causing magnetic instability as a result.
These uneven magnetic fields emerge from the sun’s surface in the form of a twisted rubber band knit carrying a lot of energy and creating tension. When magnetic lines twist and distort the flow of photon plasma could not reach the surface.
Reason for solar flare:
Above the sunspot, magnetic rings with high energy are formed that are twisted and distorted are formed. These high-energy distorted magnetic rings give birth to a high-energy storm.
When one high-energy magnetic wave superimposes with another, they become more stronger and induce a blast. This blast is intense and emerges outward from the surface and we call it a solar flare.
 Solar flare
Solar flareA solar flare is an event that frequently occurs in the sun and is equivalent to an explosion of lakhs of nuclear bombs at a time. The solar flare travels at a speed of 720,000 km per hour, releasing tremendous heat energy.
Magnetic fields spurt plasma from the sun’s surface and at certain moments large amount of light emits through the surface.
Photons emitted from the sun in the form of radiation:
After about 10 lakhs years of long journey photons emerge out of the gigantic sun as a radiation along with trillions of photons. Now they are independent and free to travel anywhere with the speed of light.
Each second trillions of photons reach the Earth and support our life directly and indirectly. Photons not only give sunlight and heat but also trigger other natural processes like rain, photosynthesis, etc.
By understanding the journey of photons from their birth in the core to reaching their destination planets, we can say that in order to give light to someone first we should burn like photons, never give up on the obstacles, and wait for the right time to reach our goal with consistent efforts.
Useful Glossary –
- Photons – Photons are discrete energy packets that constitute electromagnetic radiation. They are massless and travel at the speed of light and their behavior depends on the energy they carry.
- Plasma – Plasma is one of the fourth states of matter known. In the plasma state, electrons are no longer under the influence of atoms and form an ionized gas. Our 99% of the visible universe is plasma and this condition takes place under extreme temperature, pressure, and gravity.
- 1 Quadrillion – A quadrillion is one followed by fifteen zeroes(1,000,000,000,000,000 or 1015).
- Photosphere – The outermost region of the sun that we see with the telescope.
- Sunspot – A dark region visible on the surface of the sun.


Pingback: How tides and ocean currents are formed - Amazing Technology Blog
👍👍👍