We have traveled in trains many times but at a speed not exceeding 150 kmph. The trains we travel usually move on wheels due to the thrust generated by the friction between the wheels and the tracks. Even fast trains like bullet trains move on wheels and can attain top speeds ranging between 350 to 400 kmph.
Can you imagine a kind of bullet train that can fly and move at a speed greater than 400 kmph? Yes, there exists a bullet train that flies parallel to the track, and taking advantage of only a little air friction it can easily attain a top speed greater than 500 kmph. This train is a Maglev train and it actually flies about 4 inches above the track due to the effect of repulsion caused by the magnetic field and the wheels do not touch the track. Magnetic levitation is abbreviated to Maglev. Currently, Maglev trains are operated in Japan, South Korea, and China.
How does a maglev train move forward?
The basic principle of working of the Maglev train is magnetic repulsion between the cars and the track and magnetic levitation is achieved with the use of an electrodynamic suspension system (EDS).
Electromagnetic Suspension works on the basic principle of magnets which is like poles repel each other and unlike poles attract each other. The EMS does this in a controlled manner so that the magnetic pull is temporary or controlled.
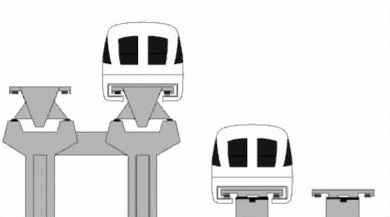
The guideway contains two sets of cross-connected metal coils wound in the number 8 pattern which forms electromagnets. The train/bogies are already manufactured as superconducting electromagnets situated beneath the train. While static the train rests on the rubber wheels. Upon start, the train starts rolling on these wheels but the moving force is created by the magnetic repulsion. The rubber wheels allow the magnets beneath the train to interact with those of the guideway. The train gets lifted 4 inches above the guideway once the speed reaches 150 kmph eliminating the rolling friction which boosts up the speed of the train.
The elevated train travels through a groove of magnetic units which controls the stability and speed of the train. Here the rolling friction is eliminated unlike other trains, only air friction comes into the picture. This technology makes the ride smoother, trains exceptionally safe, and can accelerate and decelerate much faster than conventional trains.

Advantages of Maglev technology:
- High Speed – Maglev trains are known for their high speed and can easily attain a speed of more than 400 kmph.
- Efficient – Maglev trains are proved to be efficient than those of conventional trains due to contactless levitation propulsion technology and low aerodynamic resistance. The energy loss due to the rolling friction is eliminated. They are also equipped with a highly efficient linear motor that does not consume excess power which makes them economical to operate.
- Safety – In Maglev trains, there is no derailment, the train wraps up the guideway beam and there is no risk of separation. The guideway is constructed on the flyover so operating this high-speed train doesn’t disturb the public and animals.
- Reliability – Maglev trains are the most reliable vehicles because there is no contact between the vehicle and the guideway while moving. This eliminates the wear and tear of the guideway and thus adds extended lifespan. The train uses an EMS or EDS which has very low chances of failure. The vehicle and guideway are least affected by weather conditions.
- Ecofriendly – Since the vehicle operates on electric power, there is no emission of polluting gases.
- Silent operation – The operation of the Maglev train is quieter than the other trains since it does not produce any rolling, gearing noise. The vehicle is operated on an elevated guideway and there is no usage of honks.
- Space – The guideway requires an average of 2 meters wide elevated space. The space below the flyover can be utilized for various purposes.
- Low cost of maintenance – The upfront building of the Maglev train and its guideway requires huge investment but the maintenance cost is very low because the operation of the vehicle does not cost any damage to the system and most of the parts are automatic and of high quality.
- Alternative of aircraft – The Maglev trains may be the best alternative to aircraft in the future if it is made economical and connects important cities. Aircraft emits a high amount of polluting gases into the environment.
The major difference between Maglev trains and Conventional trains:
- Maglev trains do not have engines like conventional trains.
- Maglev trains are powered by electricity whereas conventional trains are powered by electricity and fossil fuels.
- Maglev trains float over the guideway whereas conventional trains move on their wheels.
- Most of the operations of the Maglev trains are automated whereas in conventional trains it is manual.
Limitations:
- The construction of elevated guideways is costlier compared to the conventional steel railways.
- The Maglev trains can only be operated on their dedicated guideways, unlike conventional railways.
- Since Maglev trains are best suited for high speed and long journeys, constructing and operating for just 100 to 200 km is not economical.
Maglev train facts:
- The only Maglev train accident was in September 2006 near Lathen, Germany that was caused by human error on a test track.
- Currently, only Japan, South Korea, and China have built and operated Maglev trains.
- The highest recorded Maglev train speed is 603 kmph in 2015.
Why Maglev trains are only operated in few countries?
Although magnetic levitation technology has many added advantages like speed, safety, zero pollution, least maintenance Maglev trains are operational only in three countries that is Japan, South Korea, and China. Many countries have not planned yet to construct and operate Maglev train due to the involvement of high construction costs, lack of advanced technology, and various risk factors.
Useful Glossary –
- Friction – Resistance on the surface of moving object due to another object
- Levitation – the action of rising something and remain in one place in the air
- Superconducting – Superconductivity is the property of a material that allows electricity to pass through them without any resistance or negligible resistance
- Static – At rest or not moving
- Repulsion – A force that tends object to move
- Automated – Automatic in operation and does not require human interference
- Propulsion – The action of driving or moving something forward

